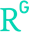This website uses cookies to ensure a better user experience.
To get more information, please read our Cookie Statement.
Metal oxide nanoparticles as solid contact in ion-selective electrodes sensitive to potassium ions
Our colleagues Nikša Krstulović, Damjan Blažeka and Julio Car, in collaboration with the scientists from the Maria Curie-Sklodowska University and Lublin University of Technology, have published a paper about metal oxide nanoparticles as solid contact in ion-selective electrodes sensitive to potassium ions. This result is important since it opens possibility of future collaboration with scientist from Poland.
Metal oxide nanoparticles as solid contact in ion-selective electrodes sensitive to potassium ions
Karolina Pietrzak, Nikša Krstulović, Damjan Blažeka, Julio Car, Szymon Malinowski, Cecylia Wardak, Talanta 243, 123335 (2022).
DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123335
In recent years, various types of nanomaterials and nanoparticles have been very popular, also in analytical chemistry for sensors preparation. In this work, ion-selective electrodes with solid contact were constructed, in which a layer of nanoparticles of selected metal oxides (zinc, copper and iron oxides) obtained by pulsed laser liquid ablation (PLAL) was placed between the glassy carbon solid electrode material and the ion-selective membrane.
The basic analytical parameters of the obtained sensors were determined using potentiometric methods. Additionally, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy method (EIS) was also used to investigate the electrical properties of the sensors. The obtained results were compared for all types of electrodes, both modified and unmodified, in order to investigate the effect of the type of nanoparticles and the thickness of their layer used as solid contact.
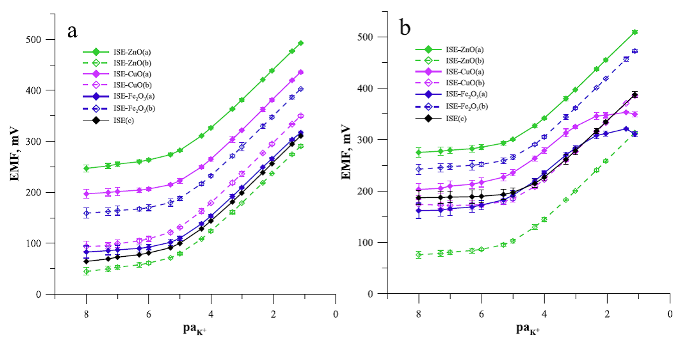
The graphs shows the calibration curves for all types of electrodes obtained (a) at the beginning of the tests (one week) and (b) after 2 months. The most favorable properties of the electrodes based on ZnONPs were found. There is also a noticeable advantage in the durability of electrodes with a thinner intermediate layer in the case of copper and iron oxide nanoparticles.
It was found that the addition of metal oxide nanoparticles improved the analytical parameters of the sensors, mainly the potential stability and electrical parameters. The best results were obtained for an electrode with an intermediate layer of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Particularly noteworthy is the significant improvement in the stability of the potential of this electrode and the long life of more than 5 months.
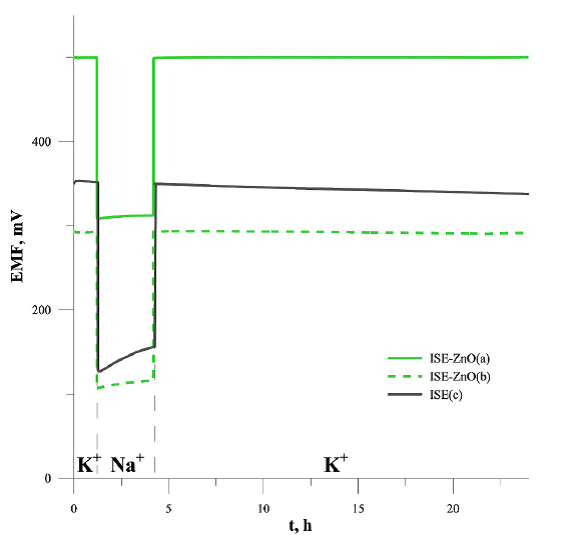
Water layer test for the SCISEs (solid contact ion-selective electrodes) with zinc oxide nanoparticles. The measurements were recorded in 1 × 10-1 mol/L KNO3 and 1 × 10-1 mol/L NaNO3. As it can be seen, ISE without nanoparticles layer exhibited noticeable potential drift after replacement of primary ions by interfering ions which indicates the formation of a water layer between the membrane and inner electrode. In the case of electrodes with an additional layer of zinc oxide nanoparticles as a solid contact, a more stable potential was observed.